Colon Cancer: Symptoms, Treatment & Care
What Is Colon Cancer?
Colon cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the colon, which is part of the large intestine. It typically develops from small growths called polyps that can turn cancerous over time. If left untreated, colon cancer can spread to nearby lymph nodes and other parts of the body. Early detection significantly improves treatment outcomes.
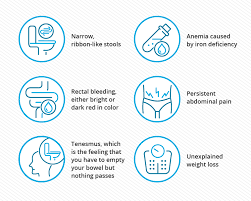
Signs & Symptoms of Colon Cancer
Colon cancer may not always show early signs. However, common symptoms include:
- Changes in bowel habits (diarrhea, constipation, or narrowing of stool)
- Blood in the stool or rectal bleeding
- Persistent abdominal discomfort (cramps, gas, or pain)
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue and weakness
- A feeling that the bowel doesn’t empty completely
Note: Having these symptoms doesn’t always mean colon cancer, but it’s important to consult a doctor if they persist.

Risk Factors for Colon Cancer
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing colon cancer, including:
- Age (most cases occur after age 50)
- Family history of colon cancer or polyps
- Personal history of inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis)
- Diet high in red or processed meat
- Lack of physical activity
- Obesity
- Smoking and heavy alcohol use
Diagnosis & Staging of Colon Cancer
Doctors use a combination of tests to detect and stage colon cancer, such as:
- Colonoscopy – the most common screening tool to examine the colon
- Biopsy – removal of tissue for testing
- Imaging tests (CT scans, MRI, PET scans) to check if cancer has spread
- Blood tests to evaluate overall health
Colon cancer staging ranges from Stage I (early, localized cancer) to Stage IV (advanced, spread to other organs).
Treatment Options for Colon Cancer
Treatment depends on the stage of colon cancer and overall health of the patient. Common treatment options include:
- Surgery – to remove cancerous parts of the colon
- Radiation therapy – often used for advanced or rectal cancers
- Chemotherapy – uses drugs to kill cancer cells or stop their growth
- Targeted therapy – focuses on specific cancer cell mechanisms
- Immunotherapy – helps the body’s immune system fight cancer
A care plan is usually personalized by a multidisciplinary team for best results.
Prevention & Early Detection of Colon Cancer
While not all cases can be prevented, the risk can be lowered by:
Early detection through colonoscopy or stool-based screening tests can help prevent colon cancer or find it at a treatable stage.
FAQs About Colon Cancer
Colon cancer develops in the colon, while colorectal cancer refers to cancer that can begin in either the colon or the rectum. Both conditions are closely related, but colon cancer specifically affects only the colon.
Yes. When diagnosed at an early stage, colon cancer can often be cured with surgery and other treatment options. Even in advanced stages, colon cancer can usually be managed with therapies that improve survival and quality of life.
For most people, colon cancer screening should begin at age 45. However, if you have higher risk factors—such as family history or certain health conditions—you may need to start earlier and undergo screening more frequently.
The survival rate for colon cancer depends on how early it is detected. Patients diagnosed with early-stage colon cancer have a much higher survival rate compared to those diagnosed at advanced stages.
Yes. You can reduce your risk of colon cancer by following a healthy lifestyle—eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption.


